Solar Systems
Solar is a proven technology which derives its energy from converting sunlight into energy. Through using Solar panels, these panels produce DC power which must be converted to AC for utilization into a building or home.
Solar systems are typically built in four different applications:
- Ground Mounted System – Meaning the system is built using frames which are secured in the ground to produce energy for supporting a customer need.
- Rooftop Mounted System – Because roof space is generally wasted space which is a liability for most customers, through properly designing a rooftop solar system the customer can gain an asset on their roof and extend the life of their roof.
- Canopy Mounted System – Through the building of canopy structures in parking lots or around the perimeter, solar can be added to any site and provide shade and weather protection for parking, while producing energy for the customer.
- Solar Tracking System – A solar tracking system enables solar panels to move (track) the trajectory of the sun for improving the system productivity.

Proven, Reliable and Extremely low cost and effective. The largest problem with ground mount is it occupies land which could be utilized for an alternative use and is visible to neighbors. Ground mount solar systems contain the following components and is usually the lowest cost to install a solar system:
- Racking – Supports solar panels and secures wiring to enable safety and weatherproofing.
- Solar Panels – Silicon panels mounted on racking which convert sunlight to DC energy.
- Inverter – Converts DC to AC energy for use by customer where system is installed. Common Types of inverters: Micro inverters are normally mounted on solar panels for converting DC to AC energy. String inverters typically consolidate up to 35KW DC (+/-) and convert to AC. Central inverters are used in larger installations.
- Wire Management – Waterproof channels attached or built-in to racking for securing wires and weatherproofing.
- Combiner/Disconnect Box – Connects multiple panels to consolidate multiple panel strings into one The disconnect enables power to be disconnected in case of emergency or during cleaning.
- Main Switch – Central system which can manually disconnect the entire solar system.
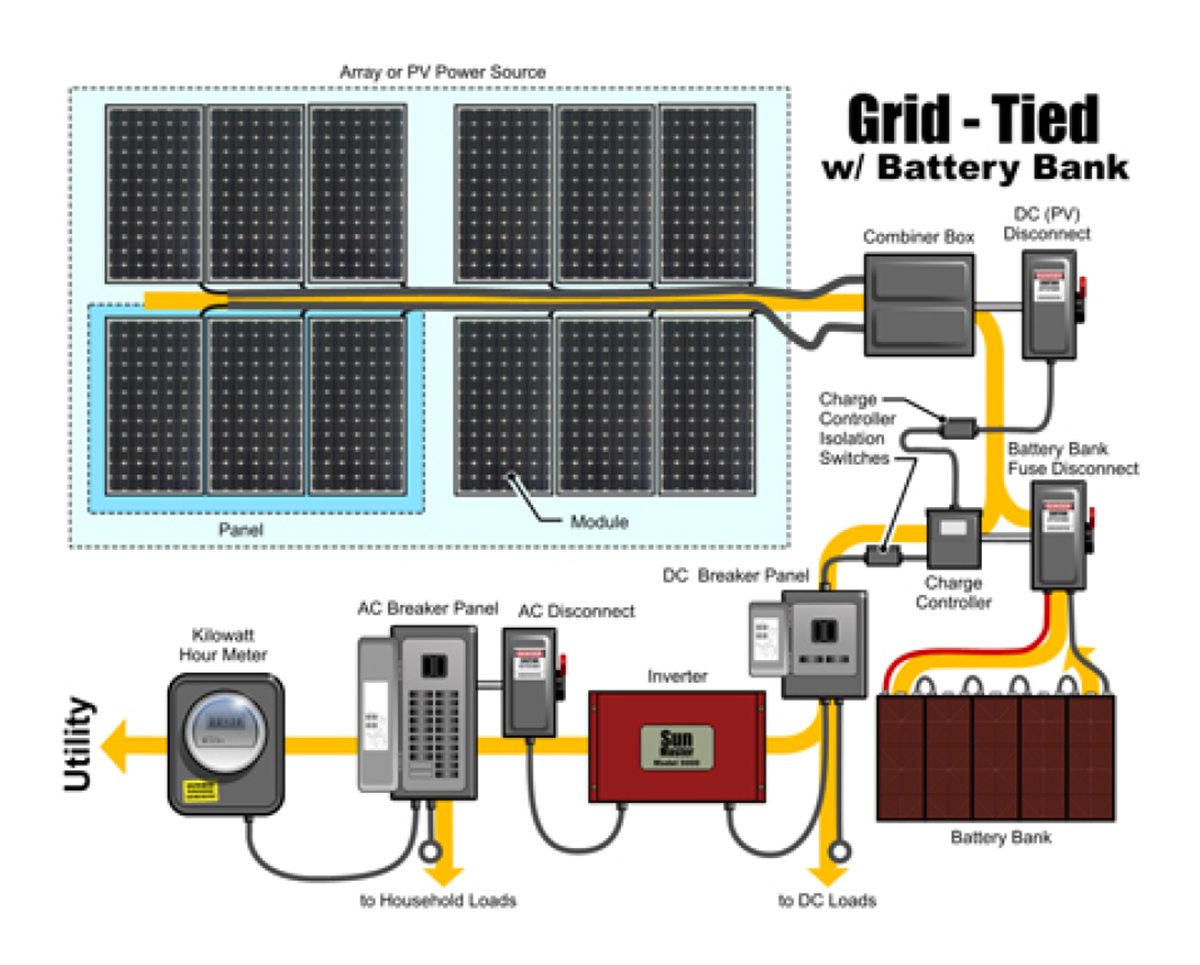
- See diagram provided for more detail, especially if you would like to use batteries.
- Codes will require fences and landscaping placed around system in most cities.

Rooftops are an economical way to utilize space one already owns and turn the liability of roof maintenance into an asset by placing solar systems on the roof. Roof mount solar systems are more expensive because of the labor and special care required when installing. Components for ground mount and rooftop mount are similar, except racking for rooftop has different design:
- Racking – Supports solar panels and mounts to the roof in most cases for structural support.
- Solar Panels – Silicon panels mounted on racking which convert sunlight to DC energy.
- Inverter – Converts DC to AC energy for use by customer where system is installed. Common Types of inverters: Micro inverters are normally mounted on solar panels for converting DC to AC energy. String inverters typically consolidate up to 35KW DC (+/-) and convert to AC. Central inverters are used in larger installations.
- Wire Management – Waterproof channels attached or built-in to racking for securing wires and weatherproofing.
- Combiner/Disconnect Box – Connects multiple panels to consolidate multiple panel strings into one The disconnect enables power to be disconnected in case of emergency or during cleaning.
- Main Switch – Central system which can manually disconnect the entire solar system.
- See diagram provided for more detail, especially if you would like to use batteries.
- Setbacks of 48 inches are required to meet Code and access for fire safety.

Canopies are an excellent way to integrate solar into parking lots and perimeter land around buildings. Although higher cost to install, benefits of supplying employees covered parking and not placing on a weak roof provide excellent benefits. Components for canopy mount is similar to rooftop and ground, where the canopy structure serves as the racking:
- Racking – Supports solar panels, inverters and wire management for the system.
- Solar Panels – Silicon panels mounted on racking which convert sunlight to DC energy.
- Inverter – Converts DC to AC energy for use by customer where system is installed. Common Types of inverters: Micro inverters are normally mounted on solar panels for converting DC to AC energy. String inverters typically consolidate up to 35KW DC (+/-) and convert to AC. Central inverters are used in larger installations.
- Wire Management – Waterproof channels attached or built-in to racking for securing wires and weatherproofing.
- Combiner/Disconnect Box – Connects multiple panels to consolidate multiple panel strings into one The disconnect enables power to be disconnected in case of emergency or during cleaning.
- Main Switch – Central system which can manually disconnect the entire solar system.
- See diagram provided for more detail, especially if you would like to use batteries.
- Codes will require different depths of drilling. Not recommended in high density rock areas due to the high cost of drilling.
![]()
Tracking is an excellent way to increase solar productivity by tracking the sun to have significantly higher perpendicular rays.
Although higher cost to install, benefits of increasing density in a space constrained area can make tracking a viable solution. Components for tracking mount system are similar to rooftop and ground, where the tracking has DC motors to turn panels:
- Pedestal Racking – Supports solar panels, rotating mechanism and wire management for the system.
- Solar Panels – Silicon panels mounted on racking which convert sunlight to DC energy.
- Inverter – Converts DC to AC energy for use by customer where system is installed. Common Types of inverters: Micro inverters are normally mounted on solar panels for converting DC to AC energy. String inverters typically consolidate up to 35KW DC (+/-) and convert to AC. Central inverters are used in larger installations.
- Wire Management – Waterproof channels attached or built-in to racking for securing wires and weatherproofing.
- Combiner/Disconnect Box – Connects multiple panels to consolidate multiple panel strings into one The disconnect enables power to be disconnected in case of emergency or during cleaning.
- Main Switch – Central system which can manually disconnect the entire solar system.
- See diagram provided for more detail, especially if you would like to use batteries.
- Tracking on roof tops is limited to roofs that can support the additional weight.
SUNBRIGHT SOLAR PARKING LOT LIGHT SERIES - IP65 waterproof, rustproof and dustproof for all weather. No Electric cost, No Underground Wires to get damaged, No concrete to cut or asphalt to repave and NO Electrical Panel upgrades and permits required. Free electricity from the Sun, stored in batteries.
Designed for outdoor use, SUNBRIGHT comes with the following features:
- Low Voltage Operating Range (48V – 60V).
- 20W – 120W (2,600 to 16,200 lumen output).
- IP65 – Waterproof, Rustproof and Dustproof.
- Programmable Dimming and Photocell controls.
- 72 hours operation without sunlight.
- 5 year unlimited use warranty.
- Type 2, Type 3, Type 4, Type 5R, Type 5QM and Type 5W lens options.
- CCT’s available: 2700K, 3500K, 4100K, 4800K, 5500K and 6500K.
- Square Pole or Round Pole available.
- No Electric cost, No cutting concrete/asphalt, GREEN Technology.
- Deep Cycle Lead Acid or Lithium Ion Phosphate (LiFePO4).